Thread Starter
#1
No rocket science to present here.
Only the basics of Steering System. Let me start & expecting everyone to participate & contribute.
Types of Steering System
1) Rack & Pinion type
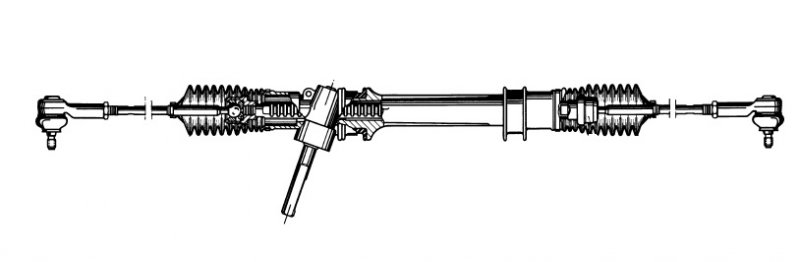
Advantages:
• simple construction
• economical and uncomplicated to manufacture
• easy to operate due to good degree of efficiency
• contact between steering rack and pinion is free of play and even internal damping is maintained
• tie rods can be joined directly to the steering rack
• minimal steering elasticity compliance
• compact (the reason why this type of steering is fitted in all European and Japanese front-wheel drive vehicles)
• the idler arm (including bearing) and the intermediate rod are no longer needed
• easy to limit steering rack travel and therefore the steering angle
Disadvantages:
• greater sensitivity to impacts
• greater stress in the case of tie rod angular forces
• disturbance of the steering wheel is easier to feel (particularly in front-wheel drives)
• tie rod length sometimes too short where it is connected at the ends of the rack (side take-off design)
• size of the steering angle dependent on steering rack travel
• this sometimes requires short steering arms resulting in higher forces in the entire steering system
• decrease in steering ratio over the steer angle associated with heavy steering during parking if the vehicle
2) Recirculating Ball type
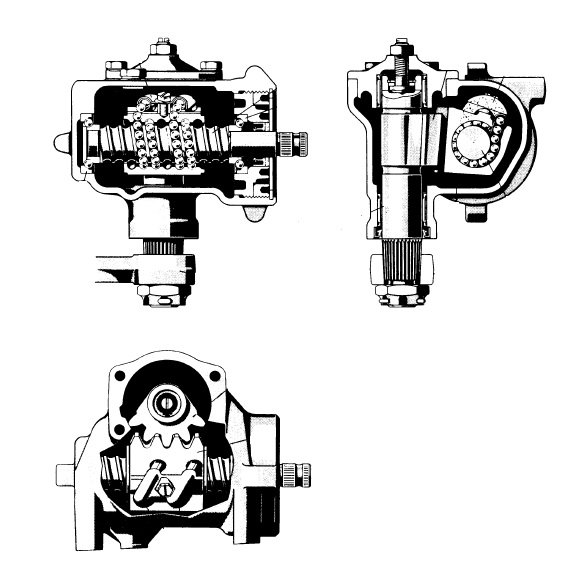
Advantages:
• Can be used on rigid axles
• Ability to transfer high forces.
• A large wheel input angle possible – the steering gear shaft has a rotation range up to ±45°, which can be further increased by the steering ratio.
• It is therefore possible to use long steering arms.
• This results in only low load to the pit-man and intermediate arms in the event of tie rod diagonal forces occurring.
• It is also possible to design tie rods of any length desired, and to have steering kinematics that allow an increase in the overall steering ratio iS with increasing steering angles. The operating forces necessary to park the vehicle are reduced in such cases.
Disadvantages:
• Higher cost
• It is heavier than Rack & Pinion steering system
• Steering feedback is not responsive
• Dead point - at a certain point the steering feedback will be zero.
These two are the important Manual steering systems.
Power assisted steering systems to follow soon.
Cheers.
Only the basics of Steering System. Let me start & expecting everyone to participate & contribute.
Types of Steering System
1) Rack & Pinion type

Advantages:
• simple construction
• economical and uncomplicated to manufacture
• easy to operate due to good degree of efficiency
• contact between steering rack and pinion is free of play and even internal damping is maintained
• tie rods can be joined directly to the steering rack
• minimal steering elasticity compliance
• compact (the reason why this type of steering is fitted in all European and Japanese front-wheel drive vehicles)
• the idler arm (including bearing) and the intermediate rod are no longer needed
• easy to limit steering rack travel and therefore the steering angle
Disadvantages:
• greater sensitivity to impacts
• greater stress in the case of tie rod angular forces
• disturbance of the steering wheel is easier to feel (particularly in front-wheel drives)
• tie rod length sometimes too short where it is connected at the ends of the rack (side take-off design)
• size of the steering angle dependent on steering rack travel
• this sometimes requires short steering arms resulting in higher forces in the entire steering system
• decrease in steering ratio over the steer angle associated with heavy steering during parking if the vehicle
2) Recirculating Ball type

Advantages:
• Can be used on rigid axles
• Ability to transfer high forces.
• A large wheel input angle possible – the steering gear shaft has a rotation range up to ±45°, which can be further increased by the steering ratio.
• It is therefore possible to use long steering arms.
• This results in only low load to the pit-man and intermediate arms in the event of tie rod diagonal forces occurring.
• It is also possible to design tie rods of any length desired, and to have steering kinematics that allow an increase in the overall steering ratio iS with increasing steering angles. The operating forces necessary to park the vehicle are reduced in such cases.
Disadvantages:
• Higher cost
• It is heavier than Rack & Pinion steering system
• Steering feedback is not responsive
• Dead point - at a certain point the steering feedback will be zero.
These two are the important Manual steering systems.
Power assisted steering systems to follow soon.
Cheers.


![Thumbs & Wink [thumbswink] [thumbswink]](https://www.theautomotiveindia.com/forums/images/smilies/Thumbs%20&%20Wink.gif)
![Surprise [surprise] [surprise]](https://www.theautomotiveindia.com/forums/images/smilies/Surprise.gif)